Insights
Different parts of the energy market
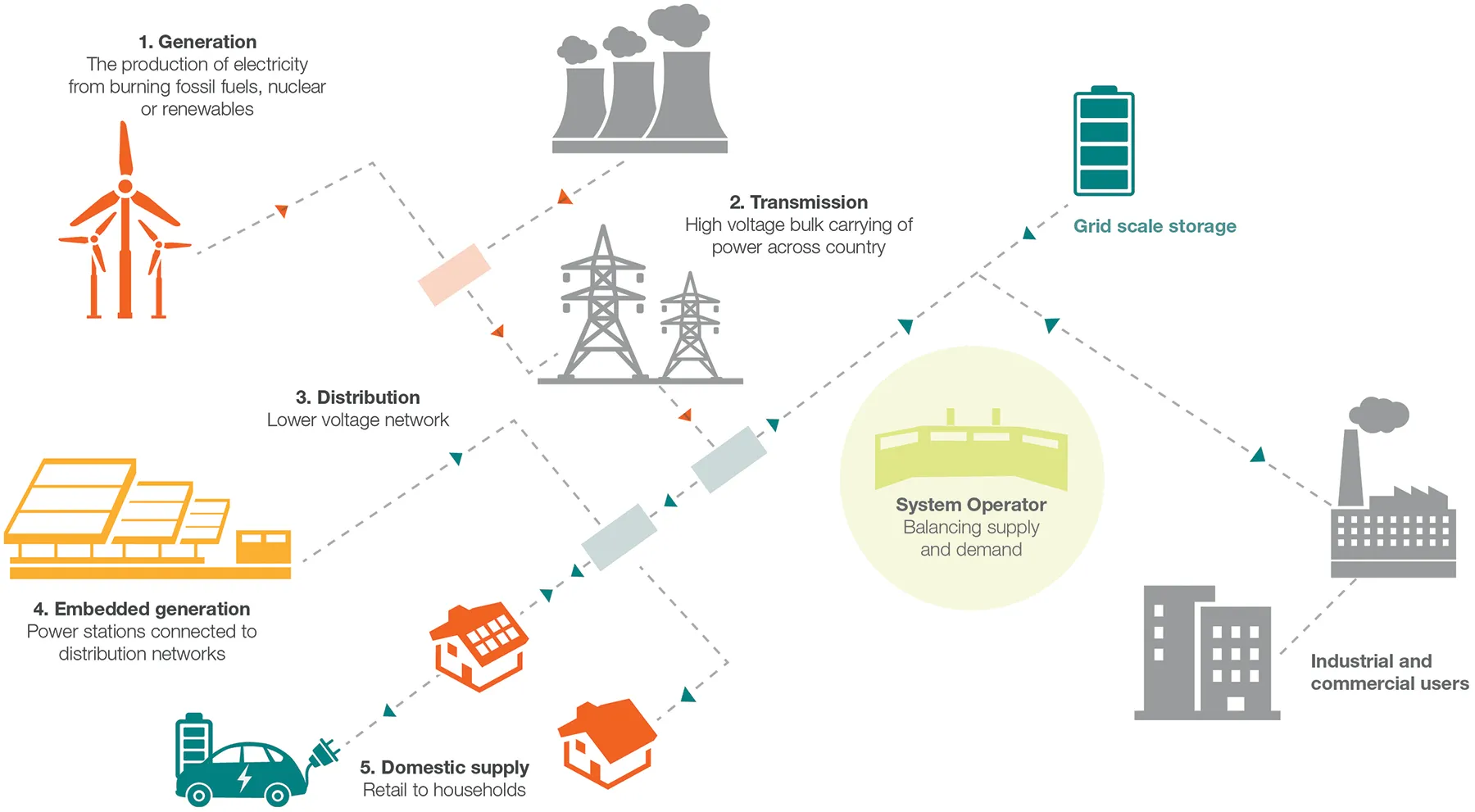
There is no single definition for an ‘energy company’. Businesses in the energy system can play a number of different roles including:

Upstream oil and gas production
This is the extraction of oil and gas out of the ground. Energy UK does not represent these activities.

Electricity generation
Our electricity is generated using a range of fuel types at power plants including gas, wind, solar, nuclear, tidal, biomass. Learn more about electricity generation.

System operation
The System Operator manages the actions happening across the energy system, including managing the many balancing markets to ensure system stability. Learn more about how the system works.

Transporting energy
Gas and Electricity Transmission Network Owners move energy via pipes or wires for long distances around the country at high voltages. Electricity Distribution Network Operators (DNOs) and Gas Distribution Networks (GDNs) take energy from the transmission network and deliver it to homes and businesses. Energy UK does not represent DNOs or GDNs. Learn more about the energy networks.

Retail suppliers
Retail suppliers supply electricity and gas to homes and businesses, and are responsible for sending bills and dealing with customer service inquiries, as well as delivering Government schemes including ECO and Warm Homes Discount. More about the energy retail market.
Some companies operate internationally and some are active in more than one area of the market.
Training courses
Energy UK runs training courses which give an understanding of the GB power system, for both those new to the industry and those wishing to broaden their knowledge.
Energy Markets
The energy market is complex and energy is traded both internationally, and within Europe. This helps the UK to ensure that we have enough energy to power our lives. The price we pay in the UK is determined by multiple factors:

Wholesale gas price
Natural gas is traded within Europe and internationally, and the price is set by market factors including supply and demand.

Wholesale electricity price
This is set by multiple factors, and is largely linked to the price of gas. Around 40% of UK electricity comes from gas.
Investment in UK energy
Electricity and gas markets in the UK are privatised. This means that companies, rather than Government, are responsible for investing billions of pounds in new energy infrastructure and maintaining the system to make sure we have the energy that we need. The sector invests £13bn annually and delivers nearly £30bn in gross value – on top of the nearly £100bn in economic activity through its supply chain and interaction with other sectors. To reach Net Zero and ensure energy security, the Climate Change Committee estimates that we need additional investment of around £20bn/year in the power sector alone, with the majority coming from the private sector
Competitive businesses have brought world-leading innovations to the UK market, from operational advances such as installing the world’s most powerful wind turbines, to demonstrating innovative ways to balance the market through the Demand Flexibility Service. A privatised energy market also means that customers can choose which companies supply their energy.